Geofencing
This week’s topic
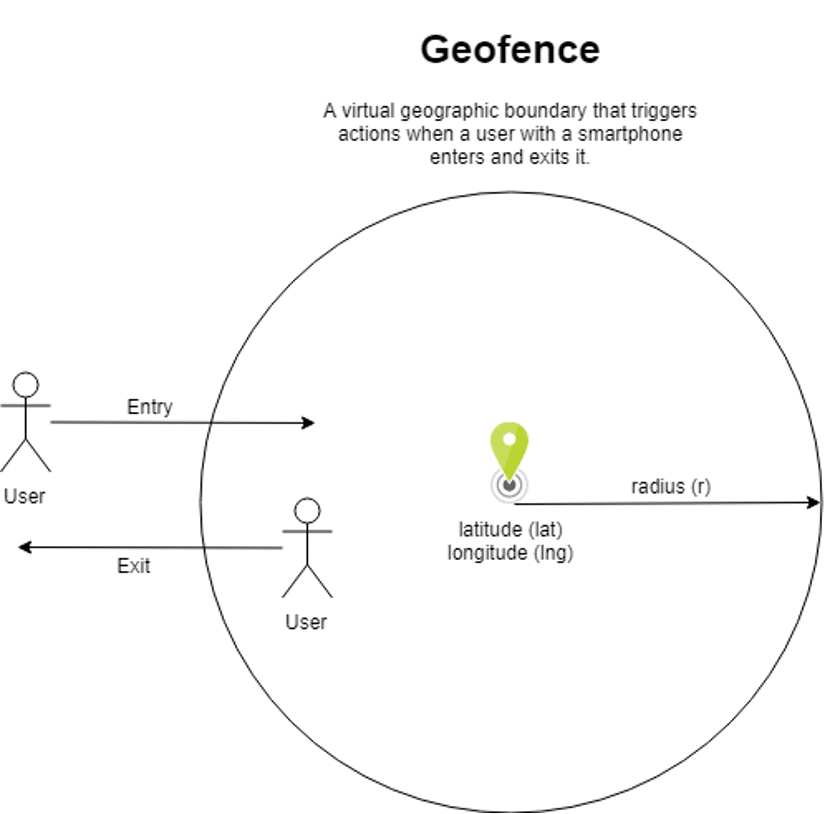
Geofencing. Geofences are virtual geographic boundaries that can be circular or polygon shaped, where a polygon is a closed shape made up of any number of straight lines, connected at points. When users with mobile devices enter or exit geofences, the device operating system (Android or iOS) signals the app which registered the geofence. The app can then respond to this event based on the use case.
Why geofencing
Geofences are often used in retail applications but can also be used in healthcare and pharma settings. The ability to make automatic real-time entry and exit detections as well as to observe the absence of detections can enable powerful context-driven workflows. Example use cases include:
- Detect medical facility entries and exits
- Detect medical facility admissions and discharges
- Detect user home entries and exits
- Detect entries and exits to high risk areas
- Detect when users are housebound for long periods of time
- Detect medical appointment adherence
- Facilitate automatic check-in for medical appointments
- Detect trial clinic visit metrics such as wait time
Geofencing is natively supported on Android and iOS mobile devices. One major benefit of geofencing is that it allows developers to build location-sensitive apps that minimally impact mobile devices battery life. Another benefit is that user privacy is increased when compared to active location tracking. This is due to the fact that, when using geofencing, user location is not known except when users interact with a geofence created by your app. Another advantage of geofencing is that it allows you to build site/facility specific workflows without the need for physical infrastructure/hardware or contracting with individual facilities.
